Research projects
Our main current and recent research projects, funded through academic grants and partnerships with public or private actors.
Current Projects
AI for predicting patent litigation (IAPLB)
Funding: CY Transfer (2025-2026)
Principal Investigator: François Maublanc
Partners: Bordeaux University
Summary: In the modern knowledge-based economy, innovation increasingly relies on patents, whose rapid growth has made it harder for firms to identify existing technologies in dense and closely related innovation spaces, thereby increasing the risk of overlooking relevant rights holders. These identification failures can be costly, as firms may face expensive litigation or unexpected licensing fees, making the ability to predict which patents are likely to be contested a key strategic tool for intellectual property management. This project addresses these challenges by using Natural Language Processing (NLP) to measure technological proximity between patents and user-provided texts, improve the prediction of litigation risk, and develop a web application for fast, visual, and in-depth patent risk analysis.
Photo credit: Markus Winkler, Unsplash license

Globalization, labor market, and developing countries (ANR GLOLADE)
Funding: ANR (2025-2029)
Principal Investigator: Giordano Mion
Thema Investigators: Giordano Mion and Pamela Bombarda
Partners: Université Paris 1 Panthéon-Sorbonne.
Summary: Over recent decades, trade liberalization has been central to reforms in developing countries, and research increasingly studies its microeconomic effects on firms and labor markets. However, most evidence focuses on formal manufacturing, overlooking the informal sector—where many workers are employed. This research project addresses these gaps by examining how policy changes, economic shocks, and supply-chain disruptions affect employment, wage gaps, informality transitions, and productivity. Using structural models, micro-econometric methods, and rich household, worker, and firm-level data, we analyze how trade policy and geopolitical or trade-related disruptions shape outcomes across formal and informal settings.
Webpage of the project here
Photo credit: Albert Chevallier Tayler, 1891, Public domain

Harmonizing actions and reforms on mobility and organization in new interactive cities (HARMONIC)
Funding: PEPR-MOBIDEC (2025-2029)
Principal Investigator: André de Palma
Partners: Strasbourg University, Université Gustave Eiffel, Institut d’aménagement et d’urbanisme de la région Île-de-France, École nationale des ponts et chaussées.
Summary: The HARMONIC project examines how major public policies on mobility, climate, and land use interact across cities and territories, identifying both their synergies and their potential contradictions. Using advanced simulation models, it recreates the movements and choices of households and firms to assess the economic, social, and environmental impacts of these policies in regions such as Greater Paris and the Strasbourg metropolitan area. Its goal is to provide decision-makers with an integrated tool that transparently evaluates how different policy scenarios affect well-being, inequalities, and environmental sustainability in cities and their surrounding territories.
Photo credit: NASA, Public domain
Laws, women, and social change (LAWSCHANGE)
Funding: CY Initiative (2025-2029)
Principal Investigator: Maëlys de la Rupelle
Partners: Tours University, Hambourg University, Namur University.
Summary: LAWSCHANGE analyses how economic inequalities can influence the legal system, particularly women’s access to justice. The project examines the societal impacts of laws relating to gender discrimination and domestic violence.
Photo credit: Alejandro Pohlenz, Unsplash License

Work from home and household inequality in labour supply and other uses of time (ANR WHIN)
Funding: ANR (2024-2029)
Principal Investigator: Elena Stancanelli (Paris School of Economics)
Thema coordinator: Olivier Donni
Partners: Institut d’études politiques de Paris, Paris School of Economics, Université La Réunion
Summary: Working from home is rapidly expanding and is expected to remain widespread in the future, with significant but still poorly understood effects on daily life, well-being, and inequality. Since the Covid pandemic, one in five workers in France works from home at least one day per week, though low-skilled workers rarely have this opportunity, deepening social divides. This project aims to fill the theoretical gap by developing a household decision-making model that incorporates remote work, combining insights from collective models, job search theory, cultural transmission, and time-use sociology, and by providing new empirical evidence across countries with different gender norms and industrial structures.
Photo credit: by vertical iberica, CC BY-SA 4.0
Land market regulations and territorial inequalities (ANR LAMARTINE)
Funding: ANR (2023-2028)
Principal Investigator Guillaume Chapelle
Summary: The LAMARTINE project aims to measure land-use regulations and assess their socioeconomic and environmental impacts. It begins by documenting and quantifying local land regulations to build a public database, then uses these data to separate the value of land from that of buildings, estimate land wealth distribution, and analyze the redistributive potential of a land tax. Finally, the project will develop spatial equilibrium models to evaluate how land regulations affect housing markets, urban form, welfare, and environmental policy design.
Photo credit: Vincent Camacho, Unsplash License

Towards a fair and sustainable taxation (HarmFisc)
Funding: CY Initiative (2023-2027)
Principal Investigator: Laurence Jacquet
Partners: University of Oslo, University of Toronto, Erasmus University Rotterdam
Summary: The HarmFisc project, funded by the 2023 CY Initiative call, explores how tax systems can be made more coherent and used as tools to address inequality, pollution, and climate change. It analyzes how individuals and firms adjust their behavior in response to tax reforms, focusing on the taxation of labor, capital, and land income across several countries. Combining theoretical modeling with international data, the project aims to provide policymakers with frameworks to design fairer and greener tax systems, including through instruments such as property taxes and environmental incentives.
Photo credit: Mika Baumeister, Unsplash License
Avoiding tax avoidance
Funding: DGFiP (2024-2025)
Principal Investigator: Sébastien Laffitte
Summary: This project on “avoided fraud” is funded by the Direction Générale des Finances Publiques (DGFiP) and explores behavioral responses to anti-avoidance tax policies using newly available administrative data.
Photo credit: by Arthur Weidmann, CC BY-SA 4.0

Past Projects [Under construction]
Recovering workers’ data to negotiate and monitor collective agreements in the platform economy (GDPOWER)
Funding: European Commission, DG Employment, European Social Fund+ (ESF+), Social Prerogatives and Specific Competencies Lines (SocPL) (2023-2025)
Consortium Coordinator: Sonila Danaj (European Centre for Social Welfare Policy and Research)
Thema Principal Investigator: Cynthia Srnec
Partners: KU Leuven, ACV-Innovatief, UCLM, Fundacion 1 de Mayo, Institute for Structural Research, Austrian Trade Union Federation, Adigital, Force Ouvriere, CoopCycle
Summary:
GDPoweR is a collaborative research project on industrial relations in the platform economy involving seven research and social partner organizations from five EU countries (Austria, Belgium, France, Poland, Spain). It centers on two sectors, ride-hailing and food delivery and explores three areas:
– The collection and use of worker data by digital labour platforms and its impact on worker well-being and their inclination to engage in collective actions.
– Strategies employed by social partners to negotiate and implement collective and company-level agreements in the platform economy. These agreements cover aspects like pay, working conditions, and the collection and use of worker data.
– The implementation, monitoring and enforcement of negotiated agreements.

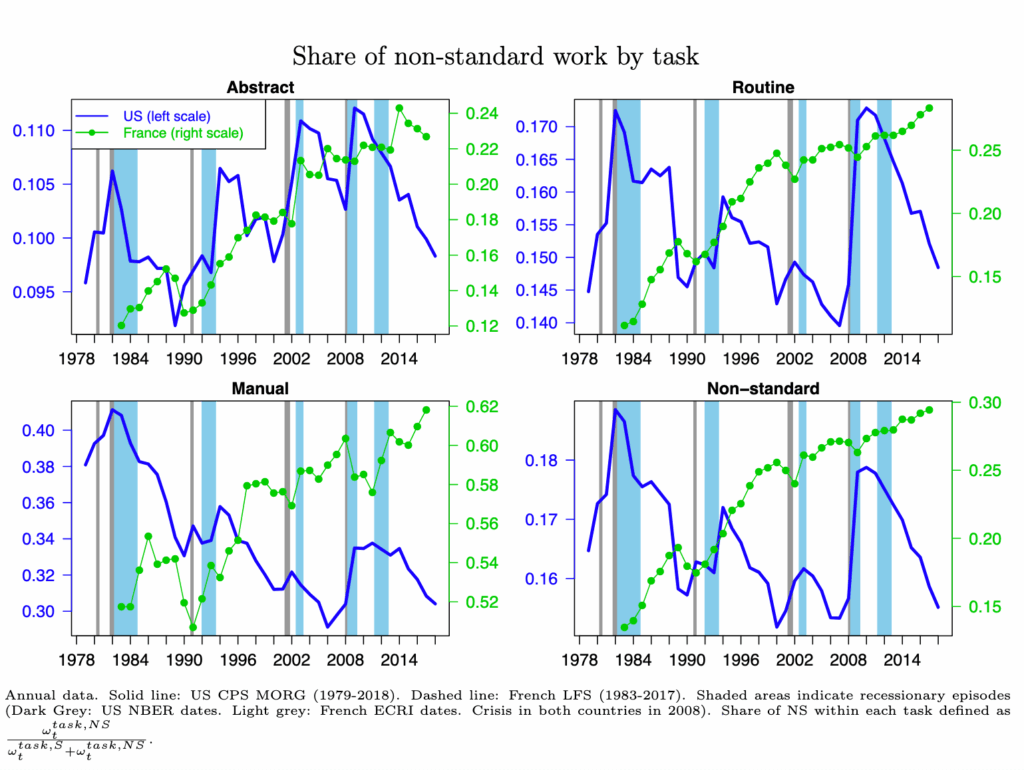
Technology and polarization of employment (ANR TOPAZE)
Funding: ANR (2018-2023)
Principal Investigator: Tepthida Sopraseuth
Partners: Sciences Po Paris
Summary: The project examines the long-term polarization of employment observed since the 1980s, characterized by the growth of high- and low-skilled jobs and the decline of routine middle-skill occupations. It first documents this phenomenon, focusing on its geographic dimension in Île-de-France and the rise of non-standard employment forms. It then analyzes how employment polarization interacts with technology and wage inequality, including productivity-wage gaps and intergenerational disparities. Finally, the project explores the social and institutional consequences of polarization, particularly its effects on gender inequalities, family structures, and political behavior.
Photo credit: Charlot et al. (2024), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.labeco.2024.102534
The impact of childhood circumstances on individual outcomes over the life-course (ANR IMCHILD)
Funding: ANR (2018-2021)
Principal Investigator: Arnaud Lefranc
Partners: AMSE (Aix-Marseille University)
Summary: The project investigates how childhood circumstances shape economic and social outcomes throughout the entire life course. It develops a theoretical framework and provides empirical evidence on how early-life conditions influence key decisions in education, occupation, and family formation, and how these, in turn, affect later outcomes such as earnings, well-being, and retirement. Through large-scale cross-country comparisons, the project seeks to uncover the mechanisms driving intergenerational mobility and inequality, offering policy insights to promote greater equality of opportunity.
Photo credit: Folsom, A.H., “Classroom Instruction at the Horace Mann School,” City of Boston Archives, CC BY-NC 3.0


